Kindergarten
1st Grade
2nd Grade
3rd Grade
4th Grade
NOTE: These are my connections only, should you find an error or find I missed something PLEASE add your thoughts in the comments.
The intention is for this to be a resource for others making the transition to these new expectations.
Resources used:
NGSS Unit: Structure and Properties of Matter
NGSS Standards:
5-PS1-1. Develop a model to describe that matter is made of particles too small to be seen5-PS1-2. Measure and graph quantities to provide evidence that regardless of the type of change that occurs when heating, cooling, or mixing substances, the total weight of matter is conserved
5-PS1-3. Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
5-PS1-4. Conduct an investigation to determine whether the mixing of two or more substances results in new substances.
Corresponding Missouri GLEs:
1st
Grade
1.1.A Scope and Sequence – Mass and Temperature
a. Given an
equal-arm balance and various objects, illustrate arrangements in which the
beam is balanced
b. Measure
and compare the mass of objects (more/less)
c. Order
objects according to mass
2nd
Grade
1.1.A Scope and Sequence – Properties of Rocks and
Soil
a. Describe
and compare the physical properties of objects by using simple tools (i.e.,
thermometer, magnifier, centimeter ruler, balance, magnet)
b. Classify
objects/substances as “one kind of material” or a mixture (e.g. m & m’s®
vs. trail mix, water vs. kool aid®)
8.1.B Scope and Sequence – Properties of
Matter/Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Describe
how tools have helped scientists make better observations (e.g., magnifiers,
balances, thermometers)
3rd
Grade
1.1.D Scope and Sequence – Investigating States of
Matter
a. Compare
the observable physical properties of solids, liquids, or gases (air) (i.e.,
visible vs. invisible, changes in shape, changes in the amount of space
occupied)
b. Identify
everyday objects/substances as solid, liquid, or gas (e.g., air, water)
c. Observe
and identify that water evaporates (liquid water changes into a gas as it moves
into the air)
d. Measure
and compare the temperature of water when it exists as a solid to its
temperature when it exists as a liquid
e. Investigate
and observe that water can change from a liquid to a solid (freeze), and back
again to a liquid (melt), as the result of temperature changes
f. Describe
the changes in the physical properties of water (i.e., shape, volume) when
frozen or melted
g. Predict
and investigate the effect of heat (thermal energy) (i.e., change in
temperature, melting, evaporation) on objects and materials
4th
Grade
1.1.A Scope and Sequence – Mixtures and Solutions
a. Describe
and compare the masses (the amount of matter in an object) of objects to the
nearest gram using balances
b. Describe
and compare the volumes (the amount of space an object occupies) of objects
using a graduated cylinder
c. Identify
situations where no two objects can occupy the same space at the same time
(e.g. water level rises when an object or substance such as a rock is placed in
a quantity of water)
d. Classify
types of materials (e.g., water, salt, sugar, iron filings, salt water) into
“like” substances (materials that have specific physical properties) or
mixtures of substances by using their characteristic properties
1.1.B Scope and Sequence – Mixtures and Solutions/
Changes on the Earth’s Surface
a. Identify
water as a solvent that dissolves materials (Do NOT assess the term solvent)
b. Observe
and describe how mixtures are mad by combining solids or liquids, or a
combination of these
c. Distinguish
between the components in a mixture/solution (e.g., trail mix, conglomerate
rock, salad, soil, salt water)
d. Describe
ways to separate the components of a mixture/solution by their properties
(i.e., sorting, filtration,
magnets, screening)
1.1.I Scope and Sequence – Mixtures and Solutions
a. Observe
that the total mass of a material remains constant whether it is together, in
parts, or in a different state
8.1.B Scope and Sequence – Mixtures and Solutions/Forms
of Energy: Electrical Circuits
a. Describe
how new technologies have helped scientists make better observations and
measurements for investigations (e.g., telescopes, magnifiers, balances,
microscopes, computers, stethoscopes, thermometers)
5th
Grade
1.1.C Scope and Sequence – Water Cycle and Weather
a. Describe
how changes in state (i.e., freezing/melting, condensation/evaporation/boiling)
provide evidence that matter is made of particles too small to be seen
1.1.D Scope and Sequence – Water cycle and Weather
a. Classify
matter as a solid, a liquid, or a gas, as it exists at room temperature, using
physical properties (i.e., volume, shape, ability to flow)
b. Predict
the effect of heat (thermal energy) on the physical properties of water as it
changes to and from a solid, liquid, or gas (i.e., freezes/melts,
evaporates/condenses/boils)
1.1.I Scope and Sequence – Water Cycle and Weather
a. Observe
the mass of water remains constant as it changes state (as evidenced in a
closed container)
1.2.A Scope and Sequence – Investigating States of
Matter
a. Identify
sources of thermal energy (e.g., Sun, stove, fire, body) that can cause solids
to change to liquids, and liquids to change to gas
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Formulate
testable questions and explanations (hypotheses)
b. Recognize
the characteristics of a fair and unbiased test
c. Conduct a
fair test to answer a question
d. Make
suggestions for reasonable improvements or extensions of a fair test
7.1.B Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make
qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Determine
the appropriate tools and techniques to collect data
c. Use a
variety of tools and equipment to gather data (e.g., hand lenses, magnets,
thermometers, metric rulers, balances, graduated cylinders, spring scales)
d. Measure
length to the nearest centimeter, mass to the nearest gram, volume to the
nearest milliliter, temperature to the nearest degree Celsius, force/weight to
the nearest Newton
e. Compare
amounts/measurements
f. Judge
whether measurements and computation of quantities are reasonable
7.1.C Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Use
quantitative and qualitative data as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use data
as support for observed patterns and relationships, and to make predictions to
be tested
c. Evaluate
the reasonableness of an explanation
d. Analyze
whether evidence supports proposed explanations
7.1.D Scope and Sequence - All Units
a.
Communicate the procedures and results of investigations and explanations
through:
⇛ oral presentations
⇛ drawings and maps
⇛ data tables
⇛ graphs (bar, single line, pictograph)
⇛ writings
8.2.A Scope and Sequence – All units
a. Research
biographical information about various scientists and inventors from different
gender and ethnic backgrounds, and describe how their work contributed to
science and technology (Assess Locally)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify
a question that was asked, or could be asked, or a problem that needed to be
solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or nonfiction of people working
alone or in groups solving everyday problems or learning through discovery)
b. Work with
a group to solve a problem, giving due credit to the ideas and contributions of
each group member (Assess Locally)
NGSS Unit: Space Systems: Stars and the Solar System
NGSS Standards:
5-PS2-1. Support an argument that the gravitational force exerted by Earth on objects is directed down.5-ESS1-1. Support an argument that the apparent brightness of the sun and stars is due to their relative distances from Earth.
5-ESS1-2. Represent data in graphical displays to reveal patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky.
Corresponding Missouri GLEs:
Kindergarten5.2.F Scope and Sequence – Weather and Seasons
a. Observe and describe daily weather: precipitation (e.g., snow, rain, sleet, fog), wind (i.e., light breezes to strong wind), cloud cover, temperature
b. Observe and describe the general weather conditions that occur during each season
6.1.A Scope and Sequence – Objects in the Sky
a. Observe and describe the presence of the Sun, Moon, and stars in the sky
b. Observe there are more stars in the sky than anyone can count and that they are scattered unevenly and vary in brightness
1st Grade
5.2.F Scope and Sequence – Observing Water and Weather
a. Observe, measure, record weather data throughout the year (i.e., cloud cover, temperature, precipitation, wind speed) by using thermometers, rain gauges, wind socks
b. Compare temperatures in different locations (e.g., inside, outside, in the sun, in the shade)
c. Compare weather data observed at different times throughout the year (e.g., hot vs. cold, cloudy vs. clear, types of precipitation, windy vs. calm)
d. Identify patterns indicating relationships between observed weather data and weather phenomena (e.g., temperature and types of precipitation, clouds and amounts of precipitation)
2nd Grade
2.1.B Scope and Sequence – Forces and Motion
a. Describe Earth’s gravity as a force that pulls objects on or near the Earth toward the Earth without touching the object
3rd Grade
1.2.A Scope and Sequence – Earth, Sun, and Moon
a. Identify sources of light energy (e.g., Sun, bulbs, flames)
b. Observe light being transferred from the source to the receiver (eye) through space
c. Identify the three things (light source, object, and surface) necessary to produce a shadow
6.1.A Scope and Sequence – Earth, Sun, and Moon
a. Describe our Sun as a star because it provides light energy to the solar system
b. Observe and identify the Moon as a reflection of light
6.2.C Scope and Sequence – Earth, Sun, and Moon
a. Observe and identify there is a day/night cycle every 24 hours
b. Describe the changes in length and position (direction) of shadows from morning to midday to afternoon
c. Describe how the Sun’s position in the sky changes the length and position of shadows
4th Grade
2.2.B Scope and Sequence – Laws of Motion
a. Determine the gravitational pull of the Earth on an object (weight) using a spring scale
5th Grade
5.2.F Scope and Sequence Water Cycle and Weather
a. Identify and use appropriate tools (i.e., thermometer, anemometer, wind vane, rain gauge, satellite images, weather maps) to collect weather data( i.e., temperature, wind speed and direction, precipitation, cloud type and cover.)
b. Identify and summarize relationships between weather data (e.g., temperature and time of day, cloud cover and temperature, wind direction and temperature) collected over a period of time.
6.1.A Scope and Sequence – Solar System
a. Observe and identify the Earth is one of several planets within a solar system that orbits the Sun
b. Observe and identify the Moon orbits the Earth in about a month
c. Identify that planets look like stars and appear to move across the sky among the stars
6.2.C Scope and Sequence – Solar System
a. Identify that the Earth rotates once every 24 hours
b. Relate changes in the length and position of a shadow to the time of day and apparent position of the Sun in the sky, as determined by Earth’s rotation
c. Relate the apparent motion of the Sun, Moon, and stars in the sky to the rotation of the Earth
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Formulate testable questions and explanations (hypotheses)
b. Recognize the characteristics of a fair and unbiased test
c. Conduct a fair test to answer a question
d. Make suggestions for reasonable improvements or extensions of a fair test
7.1.B Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Determine the appropriate tools and techniques to collect data
c. Use a variety of tools and equipment to gather data (e.g., hand lenses, magnets, thermometers, metric rulers, balances, graduated cylinders, spring scales)
d. Measure length to the nearest centimeter, mass to the nearest gram, volume to the nearest milliliter, temperature to the nearest degree Celsius, force/weight to the nearest Newton
e. Compare amounts/measurements
f. Judge whether measurements and computation of quantities are reasonable
7.1.C Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Use quantitative and qualitative data as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use data as support for observed patterns and relationships, and to make predictions to be tested
c. Evaluate the reasonableness of an explanation
d. Analyze whether evidence supports proposed explanations
7.1.D Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Communicate the procedures and results of investigations and explanations through:
⇛ oral presentations
⇛ drawings and maps
⇛ data tables
⇛ graphs (bar, single line, pictograph)
⇛ writings
8.2.A Scope and Sequence – All units
a. Research biographical information about various scientists and inventors from different gender and ethnic backgrounds, and describe how their work contributed to science and technology (Assess Locally)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify a question that was asked, or could be asked, or a problem that needed to be solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or nonfiction of people working alone or in groups solving everyday problems or learning through discovery)
b. Work with a group to solve a problem, giving due credit to the ideas and contributions of each group member (Assess Locally)
NGSS Unit: Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems
NGSS Standards:
5-PS3-1. Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.5-LS1-1. Support an argument that plants get the materials they need for growth chiefly from air and water.
5-LS2-1. Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
Corresponding Missouri GLEs:
Kindergarten3.1.D Scope and Sequence – Plants and Animals
a. Observe and compare the structures and behaviors of different kinds of plants and animals
1st Grade
1.2.C Scope and Sequence – Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Identify light from the Sun as a basic need of most plants
3.1.A Scope and Sequence – Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Identify the basic needs of most animals (i.e., air, water, food, shelter)
b. Identify the basic needs of most plants (i.e., air, water, light)
c. Predict and investigate the growth of plants when growing conditions are altered (e.g., dark vs. light, water vs. no water)
3.1.D Scope and Sequence – Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Identify and compare the physical structures of a variety of plants (e.g., stem, leaves, flowers, seeds, roots)
b. Identify and compare the physical structures of a variety of animals (e.g., sensory organs, beaks, appendages, body covering) (Do NOT assess terms: sensory organs, appendages)
c. Identify the relationships between the physical structures of plants and the function of those structures (e.g., absorption of water, absorption of light energy, support, reproduction)
d. Identify the relationships between the physical structures of animals and the function of those structures (e.g., taking in water, support, movement, obtaining food, reproduction)
3.1.E Scope and Sequence – Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Distinguish between plants and animals based on observable structures and behaviors
3rd Grade
1.2.C Scope and Sequence – Earth, Sun, and Moon/Food Chains
a. Identify the Sun as the primary source of light and food energy on Earth
3.1.A Scope and Sequence – Plants
a. Describe the basic needs of most plants (i.e., air, water, light, nutrients, temperature
3.1.D Scope and Sequence – Plants
a. Identify the major organs (roots, stems, flowers, leaves) and their functions in vascular plants (e.g., absorption, transport, reproduction)
4.2.A Scope and Sequence – Food Chains
a. Identify sunlight as the primary source of energy plants use to produce their own food
b. Classify populations of organisms as producers or consumers by the role they serve in the ecosystem
c. Sequence the flow of energy through a food chain beginning with the Sun
d. Predict the possible effects of removing an organism from a food chain
4th Grade
4.2.A Scope and Sequence – Interactions among Organisms and their Environment
a. Classify populations of organisms as producers and consumers by the role they serve in the ecosystem
b. Differentiate between the types of consumers (herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, and detrivore/decomposer)
c. Categorize organisms as predator or prey in a given ecosystem
5th Grade
3.1.D Scope and Sequence – Classification of Plants and Animals
a. Compare structures (e.g., wings vs. fins vs. legs; gills vs. lungs; feathers vs. hair vs. scales) that serve similar functions for animals belonging to different vertebrate classes
3.2.D Scope and Sequence – Classification of Plants and Animals
a. Compare the major organs/organ systems (e.g. support, reproductive, digestive, transport/circulatory, excretory, response) that perform similar functions for animals belonging to different vertebrate classes
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Formulate testable questions and explanations (hypotheses)
b. Recognize the characteristics of a fair and unbiased test
c. Conduct a fair test to answer a question
d. Make suggestions for reasonable improvements or extensions of a fair test
7.1.B Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Determine the appropriate tools and techniques to collect data
c. Use a variety of tools and equipment to gather data (e.g., hand lenses, magnets, thermometers, metric rulers, balances, graduated cylinders, spring scales)
d. Measure length to the nearest centimeter, mass to the nearest gram, volume to the nearest milliliter, temperature to the nearest degree Celsius, force/weight to the nearest Newton
e. Compare amounts/measurements
f. Judge whether measurements and computation of quantities are reasonable
7.1.C Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Use quantitative and qualitative data as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use data as support for observed patterns and relationships, and to make predictions to be tested
c. Evaluate the reasonableness of an explanation
d. Analyze whether evidence supports proposed explanations
7.1.D Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Communicate the procedures and results of investigations and explanations through:
⇛ oral presentations
⇛ drawings and maps
⇛ data tables
⇛ graphs (bar, single line, pictograph)
⇛ writings
8.2.A Scope and Sequence – All units
a. Research biographical information about various scientists and inventors from different gender and ethnic backgrounds, and describe how their work contributed to science and technology (Assess Locally)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify a question that was asked, or could be asked, or a problem that needed to be solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or nonfiction of people working alone or in groups solving everyday problems or learning through discovery)
b. Work with a group to solve a problem, giving due credit to the ideas and contributions of each group member (Assess Locally)
NGSS Unit: Earth's Systems
NGSS Standards:
5-ESS2-1. Develop a model using an example to describe ways the geosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and/or atmosphere interact.5-ESS2-2. Describe and graph the amounts and percentages of water and fresh water in various reservoirs to provide
evidence about the distribution of water on Earth
5-ESS3-1. Obtain and combine information about ways individual communities use science ideas to protect the Earth’s resources and environment.
Corresponding Missouri GLEs:
Kindergarten5.1.C Scope and Sequence – Weather and Seasons
a. Observe wind as moving air that is felt
5.2.F Scope and Sequence – Weather and Seasons
a. Observe and describe daily weather: precipitation (e.g., snow, rain, sleet, fog), wind (i.e., light breezes to strong wind), cloud cover, temperature
b. Observe and describe the general weather conditions that occur during each season
1st Grade
5.2.F Scope and Sequence – Observing Water and Weather
a. Observe, measure, record weather data throughout the year (i.e., cloud cover, temperature, precipitation, wind speed) by using thermometers, rain gauges, wind socks
b. Compare temperatures in different locations (e.g., inside, outside, in the sun, in the shade)
c. Compare weather data observed at different times throughout the year (e.g., hot vs. cold, cloudy vs. clear, types of precipitation, windy vs. calm)
d. Identify patterns indicating relationships between observed weather data and weather phenomena (e.g., temperature and types of precipitation, clouds and amounts of precipitation)
2nd Grade
5.1.A Scope and Sequence - Earth Materials: Rocks and Minerals
a. Observe and describe the physical properties (e.g., odor, color, appearance, relative grain size, texture, absorption of water) and different components (i.e., sand, clay, humus) of soils
b. Observe and describe the physical properties of rocks (e.g., size, shape, color, presence of fossils)
5.3.A Scope and Sequence – Earth materials: Rocks and Soil
a. Observe and describe ways humans use Earth’s materials (e.g., soil, rocks) in a daily life
3rd Grade
5.1.C Scope and Sequence – Investigating States of Matter
a. Identify that liquid water can be changed into a gas (vapor) in the air.
b. Identify that clouds are composed of tiny droplets of water
c. Identify air as a substance that surrounds us, taking up space and moves around us as wind
4th Grade
5.2.A Scope and Sequence- Changes in the Earth’s Surface
a. Observe and describe the breakdown of plant and animal material into soil through decomposition processes (i.e., decay/rotting, composting, digestion)
b. Identify the major landforms/bodies of water on Earth (i.e., mountains, plains, river valleys, coastlines, canyons)
c. Describe how weathering agents (e.g., water, chemicals, temperature, wind, plants) cause surface changes that create and/or change Earth’s surface materials and/or landforms/ bodies of water
d. Describe how erosion processes (i.e., action of gravity, waves, wind, rivers, glaciers) cause surface changes that create and/or change Earth’s surface materials and/or landforms/ bodies of water
e. Relate the type of landform/water body to the process by which it was formed
5.3.A Scope and Sequence – Changes in the Earth’s Surface
a. Identify the ways humans affect the erosion and deposition of Earth’s materials (e.g., clearing of land, planting vegetation, paving land construction of new buildings)
b. Propose ways to solve simple environmental problems (e.g., recycling, composting, ways to decrease soil erosion) that result from human activity
5th Grade
5.1.B Scope and Sequence – Water Cycle and Weather
a. Classify major bodies of surface water (e.g., rivers, lakes, oceans, glaciers) as fresh or salt water, flowing or stationary, large or small, solid or liquid, surface or groundwater
5.1.C Scope and Sequence – Water Cycle and Weather
a. Recognize the atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases, water, and minute particles
5.2.E Scope and Sequence – Water Cycle and Weather
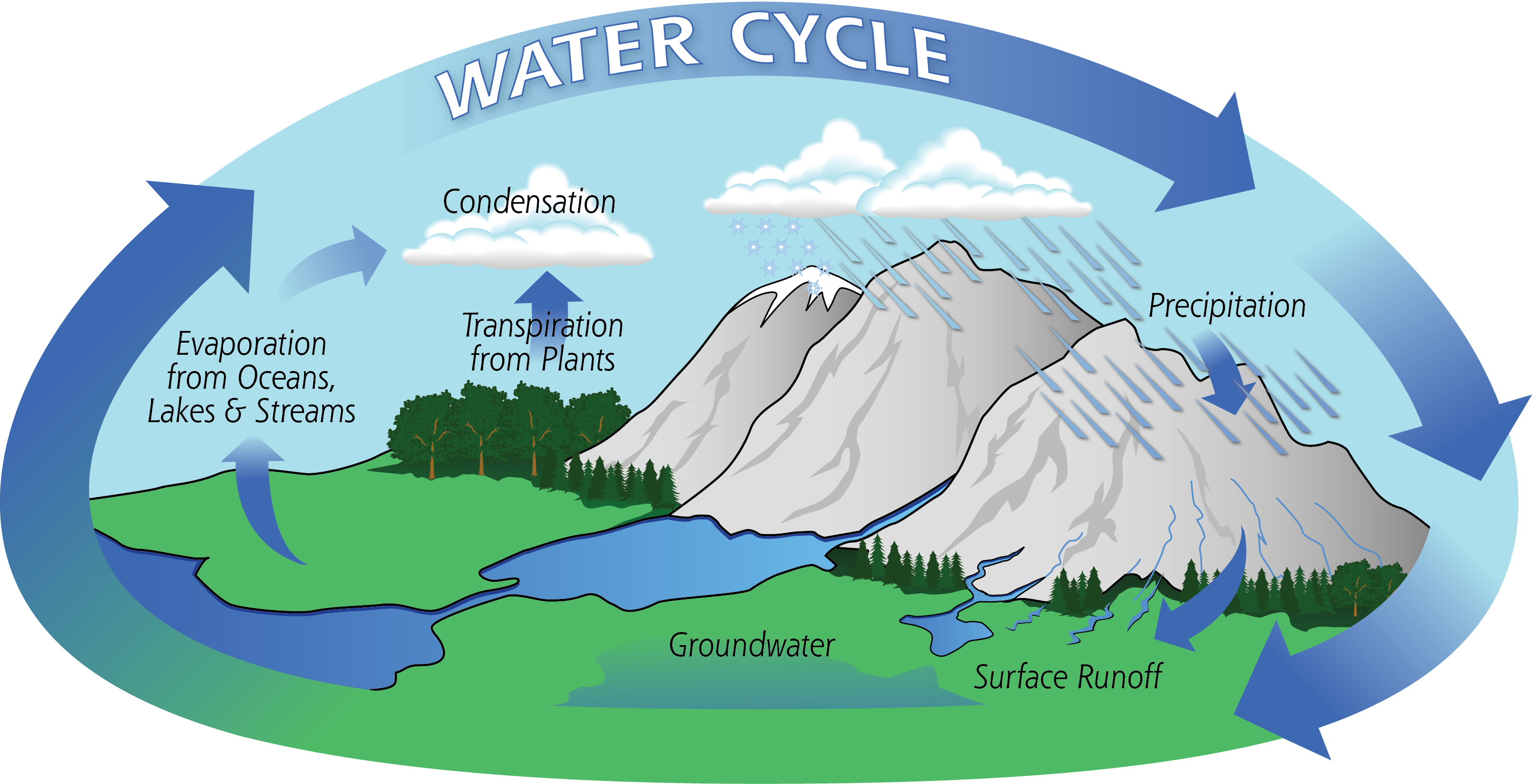
a. Describe and trace the path of water as it cycles through the hydrosphere, geosphere, and atmosphere (i.e., the water cycle: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, surface run-off/ groundwater flow)
b. Identify the different forms water can take (e.g., snow, rain, sleet, fog, clouds, dew) as it moves through the water cycle
5.2.F Scope and Sequence Water Cycle and Weather
a. Identify and use appropriate tools (i.e., thermometer, anemometer, wind vane, rain gauge, satellite images, weather maps) to collect weather data( i.e., temperature, wind speed and direction, precipitation, cloud type and cover.)
b. Identify and summarize relationships between weather data (e.g., temperature and time of day, cloud cover and temperature, wind direction and temperature) collected over a period of time.
5.3.A Scope and Sequence – Water Cycle and Weather
a. Explain how major bodies of water are important natural resources for human activity(e.g., food recreation, habitat, irrigation, solvent, transportation)
b. Describe how human needs and activities (e.g., irrigation damming of rivers, waste management, sources of drinking water) have affected the quantity and quality of major bodies of fresh water
c. Propose solutions to problems related to water quality and availability that result from human activity
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Formulate testable questions and explanations (hypotheses)
b. Recognize the characteristics of a fair and unbiased test
c. Conduct a fair test to answer a question
d. Make suggestions for reasonable improvements or extensions of a fair test
7.1.B Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Determine the appropriate tools and techniques to collect data
c. Use a variety of tools and equipment to gather data (e.g., hand lenses, magnets, thermometers, metric rulers, balances, graduated cylinders, spring scales)
d. Measure length to the nearest centimeter, mass to the nearest gram, volume to the nearest milliliter, temperature to the nearest degree Celsius, force/weight to the nearest Newton
e. Compare amounts/measurements
f. Judge whether measurements and computation of quantities are reasonable
7.1.C Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Use quantitative and qualitative data as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use data as support for observed patterns and relationships, and to make predictions to be tested
c. Evaluate the reasonableness of an explanation
d. Analyze whether evidence supports proposed explanations
7.1.D Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Communicate the procedures and results of investigations and explanations through:
⇛ oral presentations
⇛ drawings and maps
⇛ data tables
⇛ graphs (bar, single line, pictograph)
⇛ writings
8.2.A Scope and Sequence – All units
a. Research biographical information about various scientists and inventors from different gender and ethnic backgrounds, and describe how their work contributed to science and technology (Assess Locally)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify a question that was asked, or could be asked, or a problem that needed to be solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or nonfiction of people working alone or in groups solving everyday problems or learning through discovery)
b. Work with a group to solve a problem, giving due credit to the ideas and contributions of each group member (Assess Locally)





No comments:
Post a Comment