The intention is for this to be a resource for others making the transition to these new expectations.
Resources used:
NGSS Unit 1: Forces and Interactions:
NGSS Standards
K-PS2-1. Plan and conduct an investigation to compare the effects of different strengths or different directions of pushes and pulls on the motion of an object.
K-PS2-2. Analyze data to determine if a design solution works as intended to change the speed or direction of an object with a push or a pull.
Corresponding Missouri GLEs
Kindergarten
1.1.A. Scope and Sequence –
Changes in Position
a. Describe an object’s position relative to another object
(e.g., above, below, in front of, behind)
2.2.A Scope and
Sequence – Changes in Position
a. Identify ways (push, pull) to cause some objects to move
by touching them
b. Identify magnets cause some objects to move without
touching them
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Pose questions about objects, materials, organisms and
events in the environment
b. Conduct a simple investigation (fair test) to answer a
question
7.1.B. Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Make observations using simple tools and equipment (e.g.,
magnifiers/hand lenses, magnets, equal arm balances, thermometers)
c. Measure length and mass using non-standard units
d. Compare amounts/measurements
7.1.C Scope and
Sequence - All Units
a. Use
observations as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use
observations to describe relationships and patterns and to make predictions to
be tested
c. Compare
explanations with prior knowledge
7.1.D. Scope and
Sequence - All Units
a. Communicate
observations using words, pictures, and numbers
8.1.A Scope and Sequence – Properties of Matter/Weather and
Seasons
a. Observe and identify that some objects occur in nature
(natural objects); others have been designed and made by people
8.1.B. Scope and Sequence – Properties of Matter/Plants and
Animals
a. Describe how tools have helped scientists make better
observations (i.e., magnifiers)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify a question that was asked, or could be asked, or
a problem that needed to be solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or
nonfiction of individuals solving everyday problems or learning through
discovery)
b. Work with a group to solve a problem, giving due credit
to the ideas and contributions of each group member (Assess Locally)
1st Grade
1.1.A. Scope and
Sequence – Investigating Motion
a. Compare the
position of an object relative to another object (e.g., left of or right of)
b. Describe an
object’s motion as straight, circular, vibrating (back and forth), zigzag,
stopping, starting, or falling
c. Compare the
speeds (faster vs. slower) of two moving objects
2.2.A Scope and Sequence
– Investigating Motion
a. Identify the
force (i.e., push or pull) required to do work (move an object)
2.2.D Scope and
Sequence – Investigating Motion
a. Describe ways to
change the motion of an object (i.e., how to cause an object to go slower, go
faster, go farther, change direction, stop)
2nd Grade
1.1.A. Scope and Sequence – Forces and Motion
a. Describe Earth’s gravity as a force that pulls objects on
or near the Earth toward the Earth without touching the object
2.2.A Scope and
Sequence – Forces and Motion
a. Identify magnets
attract and repel each other and certain materials
b. Describe
magnetism as a force that can push or pull other objects without touching them
c. Measure (using non-standard units) and compare the force
(i.e., push or pull) required to overcome friction and move an object over
different surfaces (i.e., rough, smooth)
2.2.B Scope and
Sequence – Forces and Motion
a. Describe Earth’s gravity as a force that pulls objects on
or near the Earth toward the Earth without touching the object
2.2.D Scope and
Sequence – Forces and Motion
a. Describe the direction and amount of force (i.e.,
direction of push or pull, strong/weak push or pull) needed to change an
object’s motion (i.e., faster/slower, change in direction)
b. Describe and
compare the distances traveled by heavier/lighter objects after applying the
same amount of force (i.e., push or pull) in the same direction
c. Describe and compare the distances traveled by objects with the same mass after
applying different amounts of force (i.e., push or pull) in the same direction
2.2.F Scope and
Sequence – Forces and Motion
a. Compare and
describe the amount of force (i.e., more, less, or same push or pull) needed to
raise an object to a given height, with or without using inclined planes
(ramps) of different slopes
b. Compare and
describe the amount of force (i.e., more, less, or same push or pull) needed to
raise an object to a given height, with or without using levers
c. Apply the use of
an inclined plane (ramp) and/or lever to different real life situations in
which objects are raised
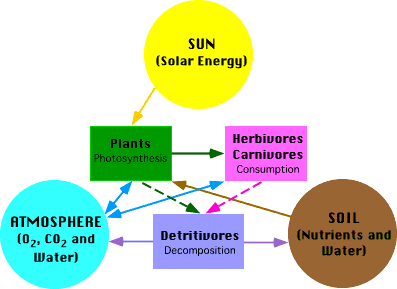
NGSS Unit 2: Relationships in Ecosystems:
NGSS Standards
K-LS1-1. Use observations to describe patterns of what plants and animals (including humans) need to survive.
K-ESS2-2. Construct an argument supported by evidence for how plants and animals (including humans) can change the environment to meet their needs.
K-ESS3-1. Use a model to represent the relationship between the needs of different plants or animals (including humans) and the places they live.
K-ESS3-3. Communicate solutions that will reduce the impact of humans on the land, water, air, and/or other living things in the local environment.
Corresponding Missouri GLEs
Kindergarten
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Pose questions about objects, materials, organisms and events in the environment
b. Conduct a simple investigation (fair test) to answer a question
7.1.B. Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Make observations using simple tools and equipment (e.g., magnifiers/hand lenses, magnets, equal arm balances, thermometers)
c. Measure length and mass using non-standard units
d. Compare amounts/measurements
7.1.C Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Use observations as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use observations to describe relationships and patterns and to make predictions to be tested
c. Compare explanations with prior knowledge
7.1.D. Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Communicate observations using words, pictures, and numbers
8.1.A Scope and Sequence – Properties of Matter/Weather and Seasons
a. Observe and identify that some objects occur in nature (natural objects); others have been designed and made by people
8.1.B. Scope and Sequence – Properties of Matter/Plants and Animals
a. Describe how tools have helped scientists make better observations (i.e., magnifiers)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify a question that was asked, or could be asked, or a problem that needed to be solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or nonfiction of individuals solving everyday problems or learning through discovery)
b. Work with a group to solve a problem, giving due credit to the ideas and contributions of each group member (Assess Locally)
1st Grade
3.3.A. Scope and Sequence – Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Identify the basic needs of most animals (i.e., air, water, food, shelter)
b. Identify the basic needs of most plants (i.e., air, water, light)
c. Predict and investigate the growth of plants when growing conditions are altered (e.g., dark vs. light, water vs. no water)
4.1.A Scope and Sequence – Characteristics of Plants and Animals
a. Identify ways man depends on plants and animals for food, clothing, and shelter
2nd Grade
5.3.A Scope and Sequence – Earth materials: Rocks and Soil
a. Observe and describe ways humans use Earth’s materials (e.g., soil, rocks) in a daily life
3rd Grade
3.3.A. Scope and Sequence – Plants
a. Describe the basic needs of most plants (i.e., air, water, light, nutrients, temperature
4th Grade
Scope and Sequence – Interactions among Organisms and their Environment
a. Identify examples in Missouri where human activity has had a beneficial or harmful effect on other organisms (e.g., feeding birds, littering vs. picking up trash, hunting/conservation of species, paving/restoring green space)
NGSS Unit 3: Weather and Climate:
NGSS Standards
K-ESS2-1. Use and share observations of local weather conditions to describe patterns over time.
K-ESS3-2. Ask questions to obtain information about the purpose of weather forecasting to prepare for, and respond to, severe weather.
K-PS3-1. Make observations to determine the effect of sunlight on Earth’s surface.
K-PS3-2. Use tools and materials to design and build a structure that will reduce the warming effect of sunlight on an area
Corresponding Missouri GLEs
Kindergarten
4.1.A. Scope and Sequence –Weather and Seasons
a. Describe how the seasons affect the behavior of plants and animals.
b. Describe how the seasons affect the everyday life of humans (e.g., clothing, activities
5.1.C Scope and Sequence – Weather and Seasons
a. Observe wind as moving air that is felt
5.2.F. Scope and Sequence – Weather and Seasons
a. Observe and describe daily weather: precipitation (e.g., snow, rain, sleet, fog), wind (i.e., light breezes to strong wind), cloud cover, temperature
b. Observe and describe the general weather conditions that occur during each season
7.1.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Pose questions about objects, materials, organisms and events in the environment
b. Conduct a simple investigation (fair test) to answer a question
7.1.B. Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Make qualitative observations using the five senses
b. Make observations using simple tools and equipment (e.g., magnifiers/hand lenses, magnets, equal arm balances, thermometers)
c. Measure length and mass using non-standard units
d. Compare amounts/measurements
7.1.C Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Use observations as support for reasonable explanations
b. Use observations to describe relationships and patterns and to make predictions to be tested
c. Compare explanations with prior knowledge
7.1.D. Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Communicate observations using words, pictures, and numbers
8.1.A Scope and Sequence – Properties of Matter/Weather and Seasons
a. Observe and identify that some objects occur in nature (natural objects); others have been designed and made by people
8.1.B. Scope and Sequence – Properties of Matter/Plants and Animals
a. Describe how tools have helped scientists make better observations (i.e., magnifiers)
8.3.A Scope and Sequence - All Units
a. Identify a question that was asked, or could be asked, or a problem that needed to be solved when given a brief scenario (fiction or nonfiction of individuals solving everyday problems or learning through discovery)
b. Work with a group to solve a problem, giving due credit to the ideas and contributions of each group member (Assess Locally)
1st Grade
5.2.F.Scope and Sequence – Observing Water and Weather
a. Observe, measure, record weather data throughout the year (i.e., cloud cover, temperature, precipitation, wind speed) by using thermometers, rain gauges, wind socks
b. Compare temperatures in different locations (e.g., inside, outside, in the sun, in the shade)
c. Compare weather data observed at different times throughout the year (e.g., hot vs. cold, cloudy vs. clear, types of precipitation, windy vs. calm)
d. Identify patterns indicating relationships between observed weather data and weather phenomena (e.g., temperature and types of precipitation, clouds and amounts of precipitation)
5.3.A Scope and Sequence – Observing Water and Weather
a. Observe and describe ways water, both as a solid and liquid, is used in everyday activities at different times of the year (e.g., bathe, drink, make ice cubes, build snowmen, cook, swim)




No comments:
Post a Comment